The Benefits of a High-Fiber Diet: Gut Health, Weight Management, and Beyond

Meta Description :
Discover the benefits of a high-fiber diet for gut health, weight management, and heart health. Learn the best fiber-rich foods backed by science.
Introduction
Fiber is one of the most overlooked nutrients in modern diets. Yet research shows it plays a vital role in gut health, blood sugar control, weight management, and long-term heart protection. According to the CDC (2023), fewer than 10% of Americans meet the daily recommended fiber intake—a major gap in modern nutrition.
This article explores the evidence-based benefits of a high-fiber diet and practical ways to increase fiber naturally.
What Is Dietary Fiber?
Dietary fiber refers to the indigestible parts of plant-based foods. There are two main types:
- Soluble fiber: dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that helps lower blood cholesterol and glucose levels.
- Insoluble fiber: adds bulk to stool, supporting regular bowel movements and gut health.
📊 A 2021 study published in Nutrients (DOI:10.3390/nu13051477) confirmed that both soluble and insoluble fibers are crucial for reducing chronic disease risk.
Benefits of a High-Fiber Diet
1. Gut Health and Microbiome
Fiber serves as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria.
👉 Harvard Health (2023) reported that people who consume 30g of fiber daily have more diverse gut microbiota, reducing risks of inflammation and IBS.
2. Weight Management
High-fiber foods are more filling, slowing digestion and reducing calorie intake.
📊 A 2022 NIH trial with 1,200 participants found those who increased fiber intake lost an average of 2.5 kg over 12 weeks without strict dieting.
3. Blood Sugar and Diabetes
Soluble fiber slows glucose absorption, preventing spikes.
👉 The American Diabetes Association (2022) recommends at least 25–30g of fiber per day to improve glycemic control.
4. Heart Health
Fiber lowers LDL cholesterol and supports cardiovascular health.
📊 According to a 2020 meta-analysis in The Lancet (DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30522-9), high-fiber diets reduce the risk of heart disease by 15–30%.
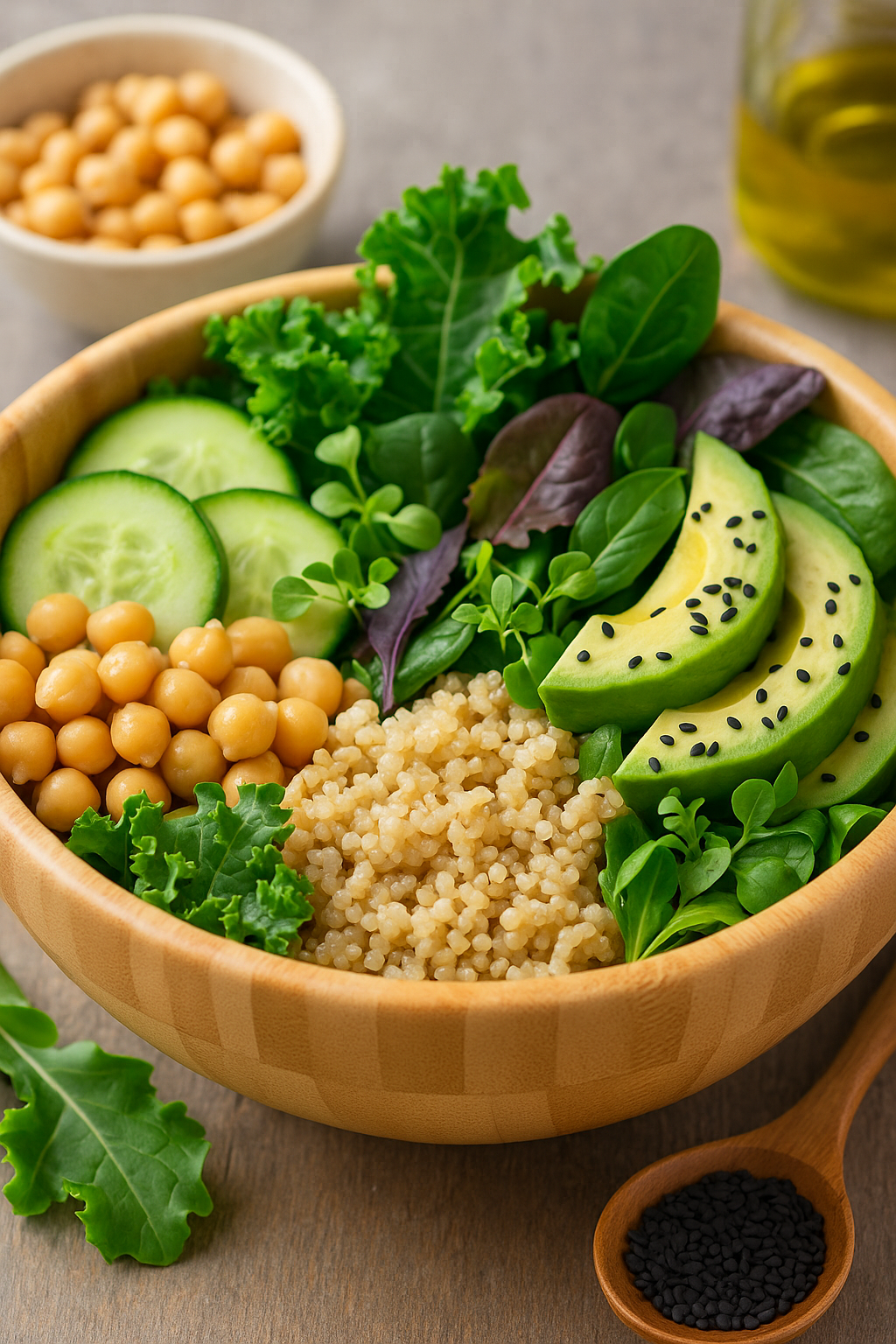
Best Fiber-Rich Foods to Include
- Legumes: lentils, chickpeas, black beans
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, barley
- Fruits: apples, pears, berries
- Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, leafy greens
- Seeds: chia, flax, sunflower
FAQ
Q1: How much fiber do I need daily?
➡️ Women: about 25g/day; Men: about 30–38g/day (Institute of Medicine, 2022).
Q2: Can too much fiber be harmful?
➡️ Excessive intake may cause bloating or gas, but adjusting gradually usually prevents this.
Q3: Is fiber supplementation effective?
➡️ Yes, but whole foods remain the best source because they provide vitamins and phytonutrients alongside fiber.
Conclusion
A high-fiber diet supports gut health, aids in weight control, stabilizes blood sugar, and protects the heart. Given that most people fall short of daily requirements, increasing fiber intake through whole foods is one of the simplest and most effective health strategies.